Cremation has become an increasingly popular choice for individuals and families seeking an alternative to traditional burial methods. One integral component of the cremation process is the cremation retort.
But what exactly is cremation retort and how does it function within the cremation process? To answer these and many other such questions we have brought a guide for you. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the world of cremation chambers, shedding light on their functionality, significance, and the overall cremation process. Happy Reading!
What is Cremation Retort?
It is a specialized chamber used in the cremation process to respectfully and efficiently cremate human remains. It is a crucial component of modern cremation facilities, designed with advanced technology to ensure a controlled and thorough cremation process.
The structure of a cremation retort typically consists of a refractory-lined chamber equipped with a primary burner. This chamber is sealed to contain the heat and prevent emissions during the cremation process. The design is essential for achieving optimal temperature control and creating an environment conducive to efficient combustion.
Moreover, this retort is a specialized chamber designed for the dignified and eco-friendly cremation of human remains, incorporating advanced technology to achieve a respectful and efficient process.
What is the structure and mechanism of Cremation Retort?
The structure and mechanism of a cremation chamber are carefully designed to facilitate a respectful and efficient cremation process. Let’s delve into the key components and workings of a typical retort:
Structure
Refractory-Lined Chamber
The retort comprises a chamber lined with refractory materials. These materials can withstand high temperatures and insulate the chamber to contain the heat.
Primary Burner
Located within the chamber, the primary burner is responsible for generating the intense heat required for the cremation process.
Sealed Enclosure
The chamber is sealed during the cremation process to prevent heat loss and control emissions. This sealed environment contributes to the efficiency of the cremation.
Mechanism
Temperature Control
Cremation chambers are equipped with sophisticated temperature control mechanisms. These controls ensure that the chamber reaches and maintains the optimal temperature for the cremation process, typically between 1,400 and 1,800 degrees Fahrenheit.
Air and Gas Flow
Proper air and gas flow are essential for combustion. Ventilation systems within the chamber facilitate the circulation of air, supporting the combustion of organic matter. This controlled flow also helps in eliminating by-products of combustion.
Controlled Combustion
The primary burner initiates the combustion process. As the temperature rises, organic matter undergoes controlled combustion. This process is crucial for the efficient breakdown of the body, leaving behind only ashes.
Cooling System
After the cremation process is complete, a cooling system allows the remains to cool down before further processing. This step ensures safe handling of the ashes.
Ash Collection and Processing
Once cooled, the remains, now in the form of ashes, are collected. Any metal implants or prosthetics are separated, and the remaining ashes are processed into a fine powder suitable for memorialization.
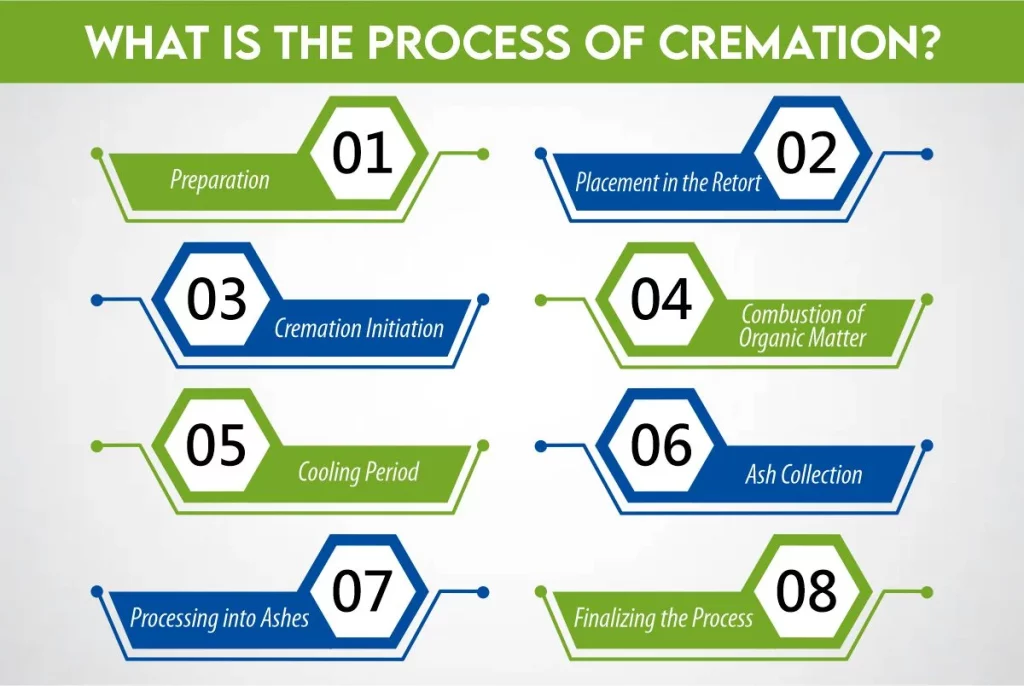
What is the process of Cremation?
Now that we understand the basics of a cremation retort, let’s explore the step-by-step process of cremation.
1- Preparation
Before the cremation process begins, the body is respectfully prepared. Non-combustible items such as pacemakers are removed to ensure safety during the cremation.
2- Placement in the Retort
The prepared body is then placed inside the retort—a specialized chamber designed for cremation. The retort is sealed to contain heat and emissions.
3- Cremation Initiation
The cremation process begins with the application of heat from the primary burner within the cremation chamber. The temperature is carefully controlled and maintained throughout the process.
4- Combustion of Organic Matter
As the temperature rises within the retort (typically between 1,400 and 1,800 degrees Fahrenheit), organic matter undergoes controlled combustion. This process breaks down the body into its elemental components.
5- Cooling Period
After the cremation is complete, the remains are left to cool. This cooling period ensures safe handling during the next steps.
6- Ash Collection
Once cooled, the remains, now in the form of ashes, are carefully collected from the cremation furnace. Metal implants or prosthetics are separated at this stage.
7- Processing into Ashes
The collected ashes undergo further processing to create a fine powder suitable for memorialization. This step may involve the use of a cremulator—a machine that grinds the remains into a consistent texture.
8- Finalizing the Process
The processed ashes are placed in an urn or container of choice. Families have the option to choose from various memorialization methods, from traditional urns to unique keepsakes.
What are the Environmental Considerations of Cremation Retort?
Cremation, including the use of a cremation chamber, is often considered to be a more environmentally friendly option compared to traditional burial methods. Here are key environmental considerations associated with the use of a retort:
Emission Controls
Modern cremation facilities are equipped with advanced filtration and scrubbing systems. These systems help control and reduce emissions, minimizing the impact on the environment. This includes the capture of pollutants and particulate matter, ensuring that the released gasses meet strict environmental standards.
Energy Efficiency
Some cremation facilities focus on implementing energy-efficient practices. This may involve the use of energy-efficient cremation retorts and other technologies to reduce the overall energy consumption of the cremation process.
Reduced Land Use
Unlike traditional burials, cremation does not require the use of land for burial plots. This reduces the demand for land and minimizes the environmental impact associated with the maintenance and use of burial grounds.
Metal Recycling
During the cremation process, any metal implants or prosthetics are separated from the remains. These metals can be recycled, contributing to sustainable practices and reducing the need for additional resource extraction.
Lower Resource Consumption
Cremation generally requires fewer resources than a traditional burial. It eliminates the need for materials such as coffins, burial vaults, and headstones, which can have environmental implications in terms of resource extraction, manufacturing, and land use.
Cremation and Carbon Footprint
While cremation does release carbon dioxide and other gasses, the controlled combustion within the retort, coupled with emission controls, aims to minimize the overall carbon footprint. Additionally, advancements in technology continue to improve the environmental performance of cremation.
Green Burial Options
Some cremation facilities offer green or eco-friendly options. This may include the use of biodegradable urns or containers, allowing for a more sustainable return of ashes to the earth.
It’s important to note that environmental considerations can vary among crematoriums, and some facilities may prioritize eco-friendly practices more than others. As technology advances, the cremation industry continues to explore and adopt greener alternatives, making cremation an increasingly environmentally conscious choice for end-of-life practices.
Why do people choose Cremation over conventional methods?
Choosing cremation as an end-of-life option is a deeply personal decision that involves considering various factors. Here are some key aspects to weigh while choosing cremation:
1- Flexibility in Memorialization
Cremation offers a wide range of memorialization options. Families can choose from traditional urns to more unique and personalized options like scattering ashes in meaningful locations or incorporating ashes into memorial jewelry. This flexibility allows for creative and customized ways to remember and honor a loved one.
2- Cost-Effectiveness
Cremation is often a more cost-effective option compared to traditional burial. It eliminates expenses associated with a burial plot, casket, headstone, and other related costs. For individuals or families mindful of budget considerations, cremation can be a financially practical choice.
3- Environmental Considerations
Many individuals today are concerned about the environmental impact of end-of-life practices. Cremation, especially when conducted in modern facilities with emission controls, is generally considered to have a lower environmental footprint compared to traditional burials. This makes it an appealing option for those seeking eco-friendly alternatives.
4- Simplicity and Efficiency
The cremation process is generally more straightforward and efficient than traditional burial. It involves fewer logistical considerations, such as the purchase of a burial plot, and the entire process can be completed in a shorter time frame. This simplicity can be comforting during a challenging time.
5- Cultural and Religious Considerations
Cultural and religious beliefs often play a significant role in end-of-life decisions. It’s essential to consider whether cremation aligns with personal or familial beliefs and practices. Many religions accept or accommodate cremation, but it’s advisable to consult with religious or spiritual leaders for guidance.
6- Memorial Services
Cremation allows for flexibility in organizing memorial services. Families can choose to hold a traditional funeral service before a cremation or opt for a memorial service afterwards. This flexibility provides an opportunity to create a meaningful and personalized tribute.
Final Verdict
In this comprehensive guide, we’ve explored the complexities of the cremation retort and its role in the cremation process. As society continues to evolve, so do our end-of-life choices. Understanding the cremation process empowers individuals to make informed decisions that align with their values and preferences.
Whether choosing cremation for its practicality, cost-effectiveness, or environmental considerations, the cremation chamber stands as a testament to modern advancements in funeral practices.

Meet Alishba, our expert Life Insurance Content Writer and Editor. With a passion for clarity, he simplify the complex world of life insurance, delivering informative, polished content tailored to our clients’ needs.



